Registered Electrical Contractor - Ireland (RECI)
Tech Stack 2020
Communication Technology Stack
With data sourced from safeelectric.ie in April 2020, we looked at the communication technology stack of 3,493 Registered Electrical Contractors, based on the contact details they provided for display.
Mobile phones are clearly the most popular communication technology amongst RECIs, with over 97% of them providing a mobile phone number. Email closely follows at over 93%. 2 out of 3 RECIs provide a landline phone number.
Almost 20% of RECIs provided a fax number, while less than 10% provided a website address. We may speculate that the RECIs with fax have been in the business for 20 or 30+ years. We may also think several reasons for the comparably low number of websites amongst RECIs.
It may be seen as unnecessary overhead, something that will take time and money, precious commodities in any business. The recession of 2008 that crashed the building boom and ended the apprenticeships of so many may have reduced the number of qualified electricians emerging over the last decade. Added to this was mass immigration of those under 35 in the construction industry.
We assume that a younger generation of RECIs are more likely to seek to promote their business or communicate with their customers through internet technologies. Whether this may, or should, include a website is open for debate. A website is undoubtedly useful and necessary for many businesses, but there are other options, and it's not for everyone.
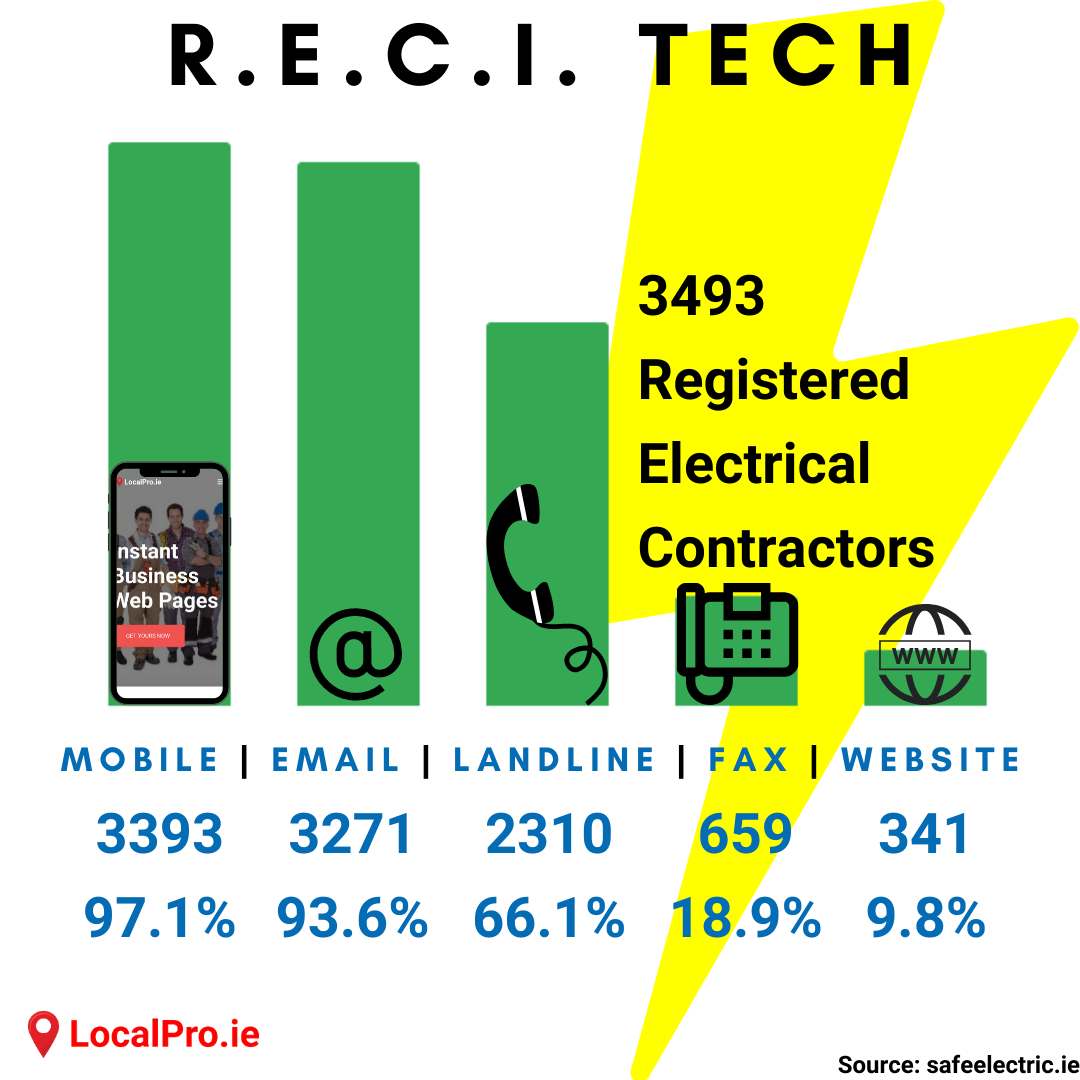
Fax ain't quite dead yet, while websites haven't really taken off amongst RECIs.
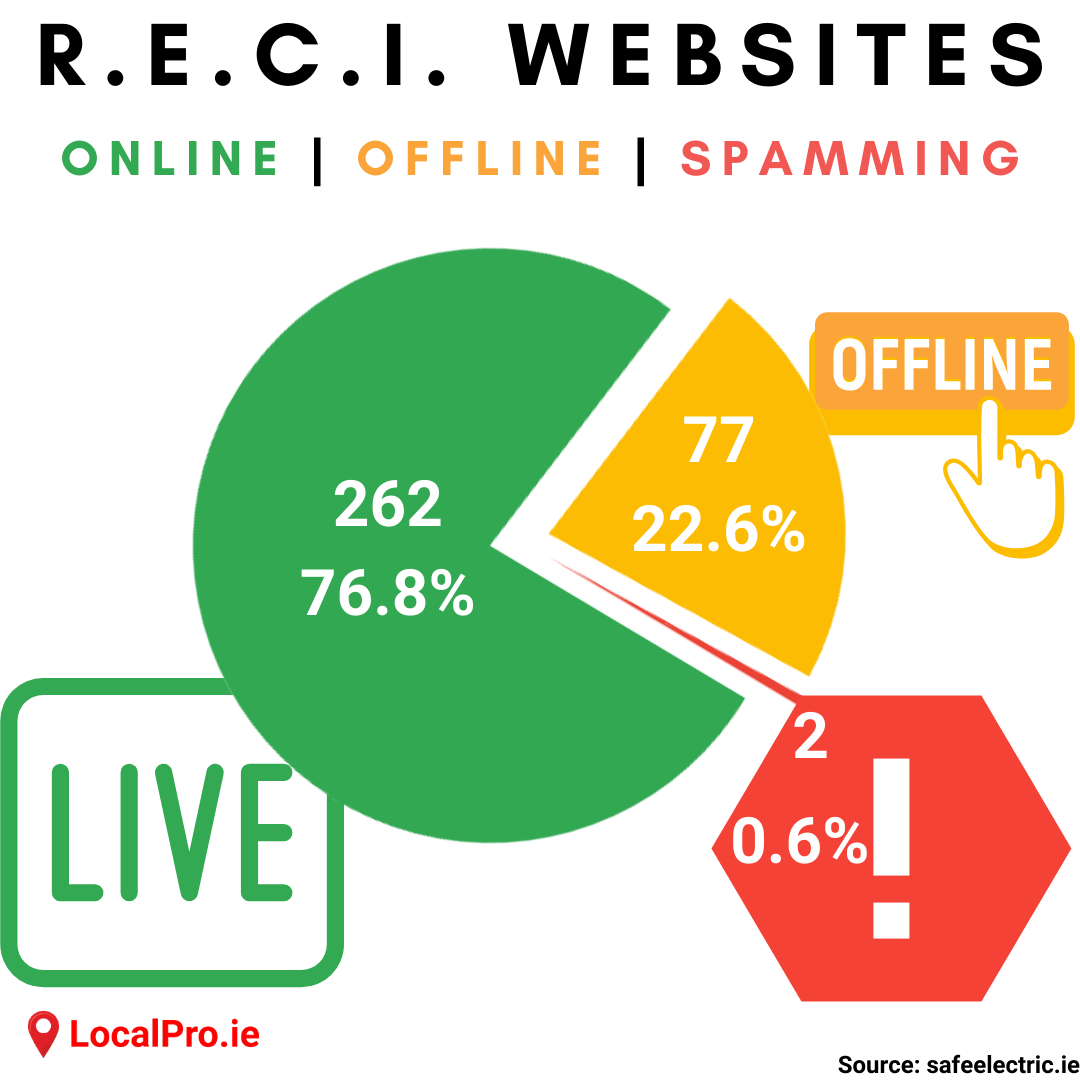
Online or Offline or Spamming*
Of the 341 RECI websites, over 20% were offline, down, dead as a dodo. 2 of them were actually redirecting to spammer websites, things like Your computer is infected! Please call tech support now! Have your credit card ready!
262 RECI websites were online, or over 75%, which may sound decent, until we look into how secure these 262 websites are. A secure site is where every page is delivered encrypted, so it is deemed safe.
It used to be the case that only webpages where you enter a password or credit card details and other such private things needed to be encrypted. Around 2018, Google decided that all pages required to be encrypted, and thus it has become the norm and standard.
* We define spamming as getting redirected to another website. Lots of stuff starts flashing on the screen like it's 3am in Vegas.
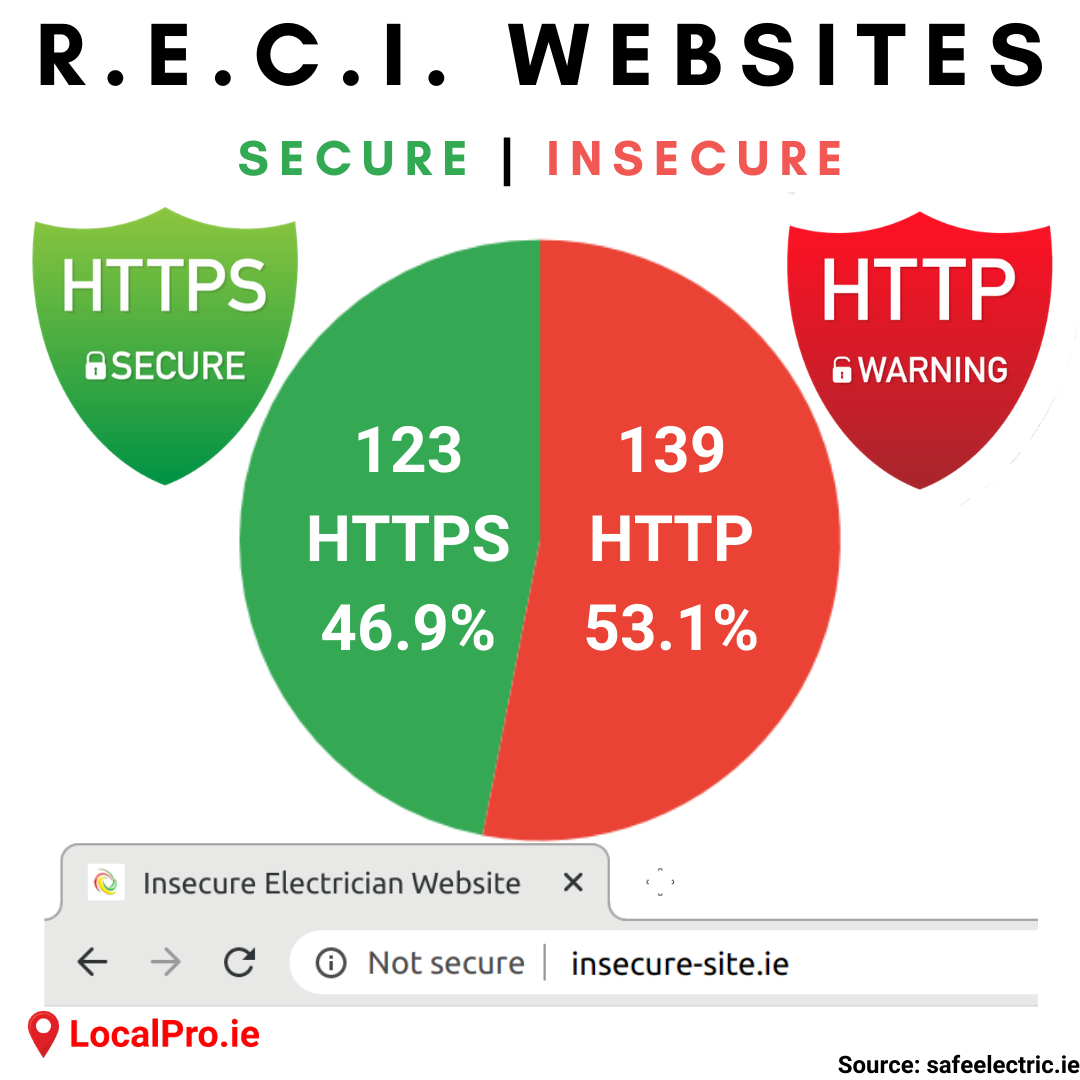
Secure or Insecure
Of the 262 RECI websites that were online at the time of our test, less than 50% were deemed secure. They delivered pages over HTTP, which is considered insecure. Pages must be delivered over HTTPS, which is deemed safe.
This is something that may not be noticed by many users of websites. Most web browsers hide the http(s) portion of website addresses. Instead, they use an icon such as an open padlock to indicate insecure http, or a closed lock to note secure https.
If a website is serving pages in insecure http, Google will deem it vulnerable. Google will rank it much lower in search results and may issue warnings about it being an insecure page. Google makes the world's number 1 search engine and web browser, both of which prominently highlight warnings about unsafe websites.
To .ie or to .com?
When it comes to a .ie or a .com domain for a website, it all depends on the business. For one, the website address that you want may already be taken under .ie or .com. For companies that are well established or trademarked, there are possibilities to appeal to attempt to claim a name under certain circumstances.
There are so many options available these days, in most cases, it's not an issue. Since March 2018, anyone Irish can register a .ie domain. .ie domains are a good idea for a business that operates solely or primarily in Ireland. Google sees .ie websites as local to, and more relevant to, people searching within Ireland.
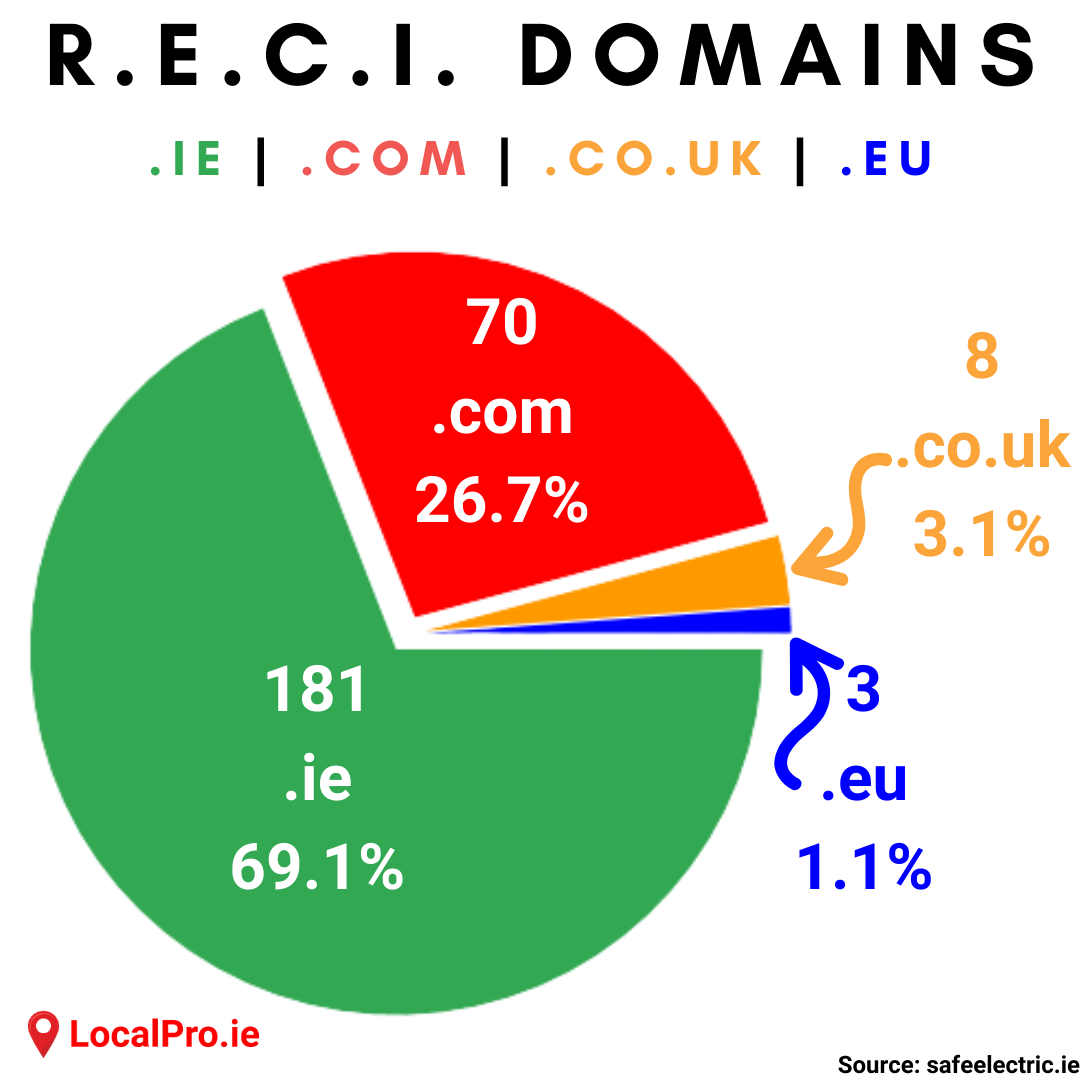
.com is best suited to international companies, but it's not a huge deal either way.
King & Queen Google
Google pretty much rules the roost when it comes to online search. As such, they heavily influence or determine a lot of the rules and standards that webpages must or should comply with if they are to be found in an online search.
Google aims to stay #1 in online search by giving the best search results. They do focus much of their efforts on giving their users the best search results. They also put some effort into upping the user's chance of clicking on a link that will get Google paid, such as Pay-Per-Click advert.
Google is increasingly answering users' search queries directly on the search results page. This means the user doesn't need to click through to a website to get the weather, for example. Some newspapers have complained about Google showing much or all of their news stories on Google search results pages. Meaning the papers were not getting badly-needed clicks to their websites.

Amazon rules online shopping. Facebook rules social-media.
Google My Business
Businesses listed on Google's My Business platform are at a considerable advantage over those who are not. They will get priority listing on the Google search results page. Registration for the Google My Business platform is free of charge. As you'd expect, there are many paid features available.
Google's My Business platform does offer some cool features, such as allowing you to set workday periods. With this, your contact phone number is only displayed in search results during these workday periods. They even offer business phone numbers so that you can keep your actual number private or offline, provide automated responses to, and get analytics data on, your callers.

SEO
Google is continuously updating its systems. Many decisions are decided by machines that figure out how best to serve search results. Likely, not even the human engineers at Google can fully explain it!
Some things are known about how Google ranks pages for listing in a search result. They want pages to load fast, very fast. Their standard measure uses a high-speed 2G or low-speed 3G connection and expects a web page to pretty much fully display in 2 to 3 seconds.
Webpages and websites should follow standard structures that are often similar to most publications. Primary standards are having just one title per web page, typically one level one header, followed by headers in descending order size of importance, with each header being followed by a reasonable amount of text.
Of significant importance, and in some cases required for regulatory compliance, is accessibility. This is ensuring that all content is available for all user groups. A most typical example is to have text describing images that are important and relevant to the understanding or use of the page. This ensures that users with limited ability to view pictures will have equal access to the webpage.

Online Presence Score
Promoting your business online is like shopping at Tesco, every little helps.
You may also like ...
LEO - Trading Online Voucher Scheme
Who's it for and how to get it? Everything you need to know about the 2020 Trading Online Voucher Scheme.
ReadInsane In The Domain Name
Our trials and tribulations whilst navigating the murky waters of internationalised domain names.
ReadBitcoin - Heads or Tails?
It was stated to be online electronic cash. Is it that or a ponzi-like pyramid scheme scam? Or is it both?
ReadComing next ...

Data Monetisation
How much is your data worth?
How much are companies earning from your data? Can you earn this money instead?

 LocalPro
LocalPro